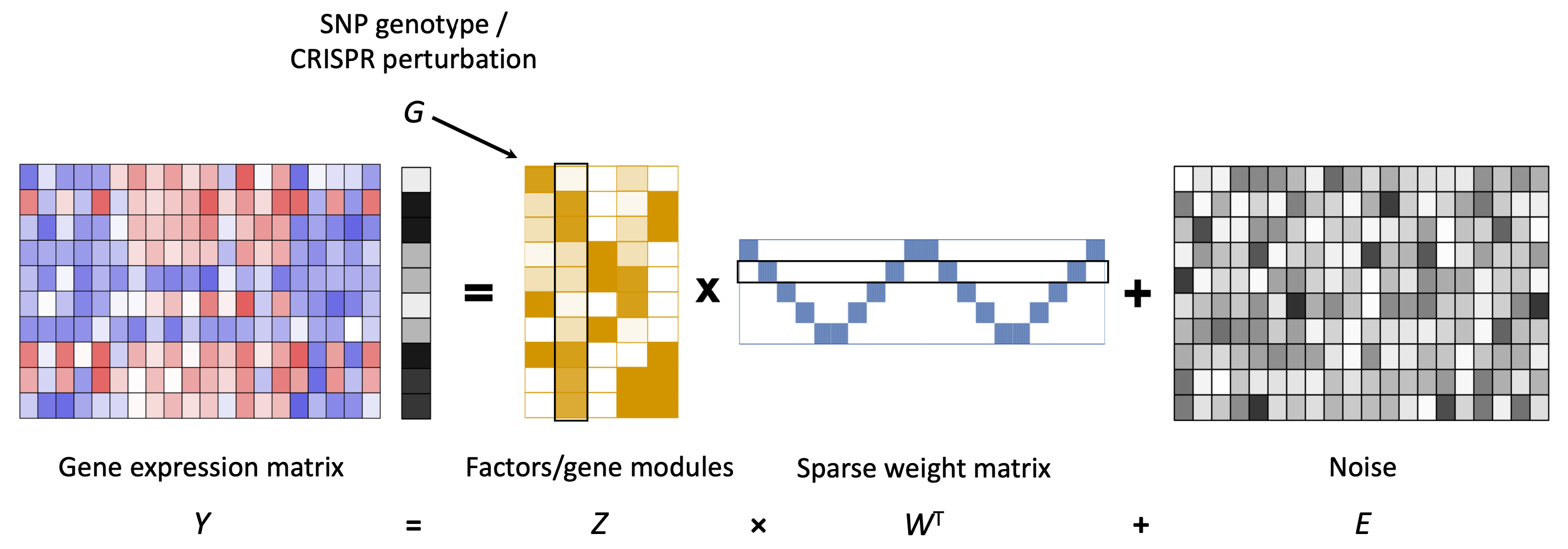
Primary Human T Cell CROP-seq Study
Source and Reference
Genome-wide CRISPR Screens in Primary Human T Cells Reveal Key Regulators of Immune Function, GEO accession: GSE119450.
Cells
Primary human CD8+ T cells from two healthy donors, with T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation.
Perturbations
CRISPR knock-out of 20 genes (2 gRNAs per gene) + 8 non-targeting gRNAs. Target genes were either found to regulate T cell responses in the genome-wide screens, or known checkpoint genes.
Analyses
- All T cells data overview, clustering analysis;
GSFA, normal-mixture prior, donor not corrected, all cells analyzed by group;
Permutation results for DGE methods;
(Archived) GSFA, normal-mixture prior, donor corrected, all cells analyzed by group;
- Stimulated T cells data overview;
Stimulated T cells pooled over 2 donors, batch effect corrected
(Archived) GSFA, normal-mixture prior;
(Archived) GSFA, spike-and-slab prior;
(Archived) Enrichment analysis on GSFA result (spike-and-slab);
- Un-stimulated T cells data overview;
Unstimulated T cells pooled over 2 donors, batch effect corrected
(Archived) GSFA, normal-mixture prior;
(Archived) GSFA, spike-and-slab prior;